Difference between revisions of "Barbados"
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
|Merch = -0 | |Merch = -0 | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bridgetown Wikipedia] | + | [[File:Barbados1721-cropped.jpg|800px]] |
| + | <p>See [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bridgetown Wikipedia]</p> | ||
=Barbados= | =Barbados= | ||
Barbados was the first major English colony in the Caribbean (in the 1620s). Though at the end of the Caribbee Islands (Lesser Antilles), Barbados remains their economic capital for more than a century. Caribbean traders often find European goods and passage to the Old World in the port of Barbados. | Barbados was the first major English colony in the Caribbean (in the 1620s). Though at the end of the Caribbee Islands (Lesser Antilles), Barbados remains their economic capital for more than a century. Caribbean traders often find European goods and passage to the Old World in the port of Barbados. | ||
Revision as of 03:07, 7 September 2022
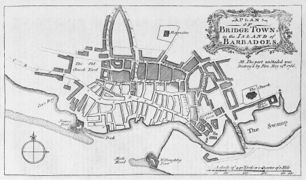
| Bridgetown, Barbados | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||

|
See Wikipedia
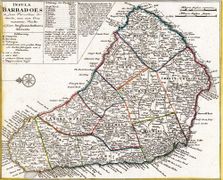
Barbados
Barbados was the first major English colony in the Caribbean (in the 1620s). Though at the end of the Caribbee Islands (Lesser Antilles), Barbados remains their economic capital for more than a century. Caribbean traders often find European goods and passage to the Old World in the port of Barbados.
Locations
Bridgetown
Timeline
18-20 Jan 1725:
- Arrived overnight
- Purchases 2 tuns cotton, 1 tun bottled rum
- John Hayden met with Captain Lockhart of His Majesty's Ship Pelican
- Rumjack arrived at port, expected to pursue
- Left in convoy with Princess Mary